1. 引言
正则表达式和 NFA (Nondeterministic Finite Automata,非确定有限状态自动机)是形式语言的两种不同的抽象表达方式。在诸如文本编辑器的高级“查找和替换”以及许多编程语言中,人们都习惯使用正则表达式来表示字符串的匹配模式。然而,当计算机执行匹配程序时,NFA 却是更加适合的一种格式。
Hyperscan 作为一款正则表达式匹配引擎,其核心部分是对 NFA 的构造和处理 —— 编译(Compilation) 将正则表达式转化为与其等价的 NFA 图并构造 NFA 引擎,扫描(Scanning)根据输入数据运行 NFA 引擎来确定匹配位置。
源码可从 GitHub Repo 下载。
2. NFA
在计算理论中,NFA 是对每个状态和输入符号可以有多个可能的下一个状态的有限状态自动机。将正则表达式转化为 NFA 图,常见的有 Thompson、Glushkov、follow,Antimirov 构造法。
2.1 Thompson 构造法
正则表达式由若干字符和运算构成,其运算只有三种:并、连接和 Kleene* 闭包。Thompson 构造法通过递归地将一个正则表达式划分成构成它的子表达式,在得到每个子表达式对应的 NFA 之后,根据子表达式之间的运算关系和一系列规则构造表达式自身对应的 NFA。
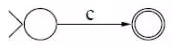
子表达式拆分,最终可得到两两类原子表达式,空表达式 ε (不消耗任一输入符号即可转移到新状态的变换) 和 单字符表达式 c (消耗任一输入字符转移到新状态的变换),其对应 NFA 图如下:
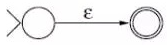
正则表达式的三种运算的对应 NFA 图如下:
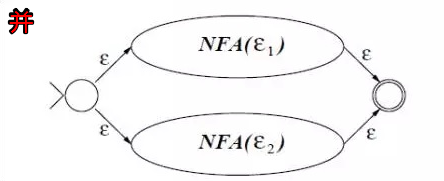
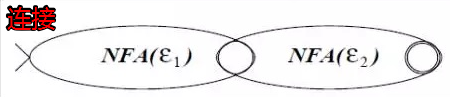
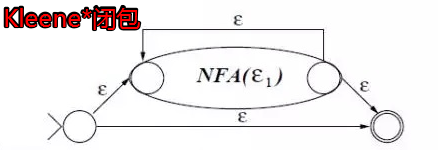
注:加括号的表达式 (ε) 直接转化为 NFA(ε) 自身即可。
例如,对正则表达式 /(a(ab)*)*+(ba)*/,用 Thompson 构造法得到的 NFA 图为
可见这样的 NFA 图状态繁多且含有大量空跳转。
2.2 Glushkov 构造法
Glushkov 构造法是基于位置的,也即是出现在表达式中的每个字符都是不同的.先对正则表达式中每个位置的字符编号(从 1 开始),对应 NFA 图中的状态,编号 0 为初始状态。然后需要递归计算各类状态集($\emptyset$(空集), $\varepsilon$ (包含空的单字符集)):
- 以函数 $\Lambda$ 判断正则表达式是否可以为空。原则
- ${\displaystyle \Lambda (\emptyset )=\emptyset }$
- ${\displaystyle \Lambda (\varepsilon )={\varepsilon }}$
- ${\displaystyle \Lambda (a)=\emptyset } \quad for \ each \ letter \ {\displaystyle a}$
- ${\displaystyle \Lambda (e+f)=\Lambda (e)\cup \Lambda (f)}$
- ${\displaystyle \Lambda (e\cdot f)=\Lambda (e)\cdot \Lambda (f)}$
- ${\displaystyle \Lambda (e^{*})={\varepsilon }}$
- 以函数 ${\displaystyle P}$ 计算正则表达式的起始状态集。原则
- ${\displaystyle P(\emptyset )=P(\varepsilon )=\emptyset }$
- ${\displaystyle P(a)={a}} \quad for \ each \ letter \ {\displaystyle a}$
- ${\displaystyle P(e+f)=P(e)\cup P(f)}$
- ${\displaystyle P(e\cdot f)=P(e)\cup \Lambda (e)P(f)}$
- ${\displaystyle P(e^{*})=P(e)}$
- 以函数 ${\displaystyle D}$ 计算正则表达式的结束状态集。原则
- ${\displaystyle D(\emptyset )=D(\varepsilon )=\emptyset }$
- ${\displaystyle D(a)={a}} \quad for \ each \ letter \ {\displaystyle a}$
- ${\displaystyle D(e+f)=D(e)\cup D(f)}$
- $D(e\cdot f)= D(f)\cup D(e) \Lambda(f)$
- ${\displaystyle D(e^{*})=D(e)}$
- 以函数 ${\displaystyle F}$ 计算正则表达式的所有连接状态对(长度为 2)集合。原则
- ${\displaystyle F(\emptyset )=F(\varepsilon )=F(a)=\emptyset } \quad for \ each \ letter \ {\displaystyle a}$
- ${\displaystyle F(e+f)=F(e)\cup F(f)}$
- ${\displaystyle F(e\cdot f)=F(e)\cup F(f)\cup D(e)P(f)}$
- ${\displaystyle F(e^{*})=F(e)\cup D(e)P(e)}$
得到最终的 P、D、F 后,从开始状态 0 到 P 中每个状态都加一个跳转,D 中所有状态都标记为结束状态,F 中每个状态对之间也都加一个跳转,如此就得到了对应的 Glushkov NFA 图。另外若 ${\displaystyle \Lambda ={\varepsilon }}$ 则表示该图可为空。
还以正则表达式 $e = (a(ab)) + (ba)$ 为例,构造过程中可视为 $e’=(a_1(a_2b_3))+(b_4a_5)$,并且
可以得到
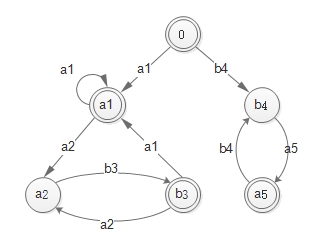
最终版
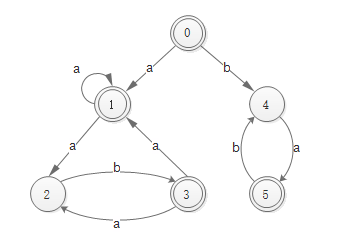
Glushkov NFA 十分简洁,不含空跳转,且一个状态的所有进入条件都相同。Hyperscan 使用 Glushkov 方法构造 NFA 图。
3. 编译
3.1 主流程
关键函数 hs_compile_multi_int() 实现如下:
hs_error_t
hs_compile_multi_int(const char *const *expressions, // 正则表达式/模式串
const unsigned *flags, // 编译标记
const unsigned *ids, // 模式串唯一标识(序号)
const hs_expr_ext *const *ext, // 扩展标记
unsigned elements, // 模式串数量
unsigned mode, // 扫描模式
const hs_platform_info_t *platform, // 目标平台架构信息
hs_database_t **db, // 模式数据库
hs_compile_error_t **comp_error, // 错误信息收集
const Grey &g) // 许多开关与限制条件
{
// 检查参数和标记
......
// 当设置返回匹配的起始位置时,设置其精度
// This function is simply a wrapper around both the parser and compiler
bool isStreaming = mode & (HS_MODE_STREAM | HS_MODE_VECTORED);
bool isVectored = mode & HS_MODE_VECTORED;
unsigned somPrecision = getSomPrecision(mode);
// 设置目标平台架构,默认为当前平台的架构信息
target_t target_info = platform ? target_t(*platform)
: get_current_target();
// 构建编译的上下文
CompileContext cc(isStreaming, isVectored, target_info, g);
// 声明一个 NFA Graph
NG ng(cc, elements, somPrecision);
try {
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < elements; i++) {
try {
// 从正则表达式构建 NFA 图
addExpression(ng, i, expressions[i], flags ? flags[i] : 0,
ext ? ext[i] : nullptr, ids ? ids[i] : 0);
} catch (CompileError &e) {
/* Caught a parse error:
* throw it upstream as a CompileError with a specific index */
e.setExpressionIndex(i);
throw; /* do not slice */
}
}
// 依据 NFA 图构建模式数据库
unsigned length = 0;
struct hs_database *out = build(ng, &length);
*db = out;
*comp_error = nullptr;
return HS_SUCCESS;
}
catch (...) {
// 处理抛出的各种异常
......
}
}
3.2 正则表达式转化 NFA 图
3.2.1 数据结构
正则表达式在 Hyperscan 的存在形式:
class ParsedExpression : noncopyable {
public:
ParsedExpression(unsigned index, const char *expression, unsigned flags,
ReportID report, const hs_expr_ext *ext = nullptr);
/** 标记、限制条件等信息 */
ExpressionInfo expr;
/** 指向表达式树形结构的根节点(构建函数 parse() 目前只会抛出一个解析异常而失败) */
std::unique_ptr<Component> component;
};
NFA 图的数据结构:
/** 封装 NFA 图, 存储顶点及其它数据。边的格式如下:
*
* - (start, startDs)
* - (startDs, startDs) (self-loop)
* - (accept, acceptEod)
*/
class NGHolder : public ue2_graph<NGHolder, NFAGraphVertexProps,
NFAGraphEdgeProps> {
public:
explicit NGHolder(nfa_kind kind);
NGHolder(void) : NGHolder(NFA_OUTFIX) {};
virtual ~NGHolder(void);
nfa_kind kind; /* 在 NFA 引擎中充当的角色 */
static const size_t N_SPECIAL_VERTICES = N_SPECIALS;
public:
const vertex_descriptor start; //!< Anchored start vertex.
const vertex_descriptor startDs; //!< Unanchored start-dotstar vertex.
const vertex_descriptor accept; //!< Accept vertex.
const vertex_descriptor acceptEod; //!< Accept at EOD vertex.
vertex_descriptor getSpecialVertex(u32 id) const;
};
其中,点的存在形式如下:
class vertex_descriptor : totally_ordered<vertex_descriptor> {
public:
vertex_descriptor() : p(nullptr), serial(0) { }
explicit vertex_descriptor(vertex_node *pp)
: p(pp), serial(pp->serial) { }
operator bool() const { return p; }
bool operator<(const vertex_descriptor b) const {
if (p && b.p) {
/* no vertices in the same graph can have the same serial */
assert(p == b.p || serial != b.serial);
return serial < b.serial;
} else {
return p < b.p;
}
}
bool operator==(const vertex_descriptor b) const {
return p == b.p;
}
friend size_t hash_value(vertex_descriptor v) {
using boost::hash_value;
return hash_value(v.serial);
}
private:
vertex_node *raw(void) { return p; }
vertex_node *p;
u64a serial; // 序号
friend ue2_graph;
};
struct vertex_node : public boost::intrusive::list_base_hook<> {
explicit vertex_node(u64a serial_in) : serial(serial_in) { }
VertexPropertyType props;
const u64a serial; /* 顶点序号 */
vertex_edge_list<in_edge_hook> in_edge_list; /* 入边。不归属该顶点 */
vertex_edge_list<out_edge_hook> out_edge_list;/* 出边。归属该顶点,需要管理释放 */
~vertex_node() {
out_edge_list.clear_and_dispose(delete_disposer());
}
}
3.2.2 流程
void addExpression(NG &ng, unsigned index, const char *expression,
unsigned flags, const hs_expr_ext *ext, ReportID id) {
const CompileContext &cc = ng.cc;
// Ensure that our pattern isn't too long (in characters).
if (strlen(expression) > cc.grey.limitPatternLength) {
throw CompileError("Pattern length exceeds limit.");
}
// Do per-expression processing: errors here will result in an exception
// being thrown up to our caller
ParsedExpression pe(index, expression, flags, id, ext);
dumpExpression(pe, "orig", cc.grey);
// 合法性检查
......
// If this expression is a literal, we can feed it directly to Rose rather
// than building the NFA graph.
if (shortcutLiteral(ng, pe)) {
DEBUG_PRINTF("took literal short cut\n");
return;
}
// 构建 NFA 图
auto built_expr = buildGraph(ng.rm, cc, pe);
if (!built_expr.g) {
throw CompileError("Internal error.");
}
if (!pe.expr.allow_vacuous && matches_everywhere(*built_expr.g)) {
throw CompileError("Pattern matches empty buffer; use "
"HS_FLAG_ALLOWEMPTY to enable support.");
}
// 消费掉这个 NFA 图,将其添加到 NG 的 smallwrite builder
if (!ng.addGraph(built_expr.expr, std::move(built_expr.g))) {
DEBUG_PRINTF("NFA addGraph failed on ID %u.\n", pe.expr.report);
throw CompileError("Error compiling expression.");
}
}
BuiltExpression buildGraph(ReportManager &rm, const CompileContext &cc,
const ParsedExpression &pe) {
const auto builder = makeNFABuilder(rm, cc, pe);
// 设定起始(包含锚定和浮动两类)状态集和可接受状态集(即结束状态集)。
// 一个浮动起始状态可以是任一起始状态的后继
const auto bs = makeGlushkovBuildState(*builder, pe.expr.prefilter);
// Informs the Glushkov build process of the positions used by this component.
// Map position IDs to characters/components
pe.component->notePositions(*bs);
// Wire the start dotstar state to the firsts
connectInitialStates(*bs, pe);
// Build the rest of the FOLLOW set
vector<PositionInfo> initials = {builder->getStartDotStar(),
builder->getStart()};
pe.component->buildFollowSet(*bs, initials);
// Wire the lasts to the accept state
connectFinalStates(*bs, pe);
// Create our edges
bs->buildEdges();
// 一个表达式,一个 NFA 图
BuiltExpression built_expr = builder->getGraph();
// Convert temporary assert vertices (from construction method) to edge-based flags.
removeAssertVertices(rm, *built_expr.g, built_expr.expr);
return built_expr;
}
3.3 NFA 图转化模式数据库
3.3.1 数据结构
模式数据库的存在形式如下:
struct hs_database {
u32 magic;
u32 version;
u32 length;
u64a platform;
u32 crc32;
u32 reserved0;
u32 reserved1;
u32 bytecode; // offset relative to db start
u32 padding[16];
char bytes[];
};
3.3.2 流程
struct hs_database *build(NG &ng, unsigned int *length) {
auto rose = generateRoseEngine(ng);
if (!rose) {
throw CompileError("Unable to generate bytecode.");
}
*length = rose.size();
if (!*length) {
throw CompileError("Internal error.");
}
const char *bytecode = (const char *)(rose.get());
const platform_t p = target_to_platform(ng.cc.target_info);
struct hs_database *db = dbCreate(bytecode, *length, p);
if (!db) {
throw CompileError("Could not allocate memory for bytecode.");
}
return db;
}
static
hs_database_t *dbCreate(const char *in_bytecode, size_t len, u64a platform) {
size_t db_len = sizeof(struct hs_database) + len;
struct hs_database *db = (struct hs_database *)hs_database_alloc(db_len);
if (hs_check_alloc(db) != HS_SUCCESS) {
hs_database_free(db);
return nullptr;
}
// So that none of our database is uninitialized
memset(db, 0, db_len);
// we need to align things manually
size_t shift = (uintptr_t)db->bytes & 0x3f;
db->bytecode = offsetof(struct hs_database, bytes) - shift;
char *bytecode = (char *)db + db->bytecode;
db->magic = HS_DB_MAGIC;
db->version = HS_DB_VERSION;
db->length = len;
db->platform = platform;
// Copy bytecode
memcpy(bytecode, in_bytecode, len);
db->crc32 = Crc32c_ComputeBuf(0, bytecode, db->length);
return db;
}
可见数据库只是一个带一些辅助信息的序列化了的 Rose 引擎。
4. 扫描
4.1 扫描流程
HS_PUBLIC_API
hs_error_t HS_CDECL hs_scan(const hs_database_t *db, // 模式数据库
const char *data, // 目标数据
unsigned length, // 目标数据大小
unsigned flags, // 留待将来使用
hs_scratch_t *scratch, // 草稿空间
match_event_handler onEvent, // 回调函数
void *userCtx) // 预定义的传给回调函数的指针
{
// 检查参数
......
const struct RoseEngine *rose = hs_get_bytecode(db);
......
if (unlikely(markScratchInUse(scratch))) {
return HS_SCRATCH_IN_USE;
}
if (rose->minWidth > length) {
unmarkScratchInUse(scratch);
return HS_SUCCESS;
}
// 预加载数据至内存中
prefetch_data(data, length);
/* populate core info in scratch */
populateCoreInfo(scratch, rose, scratch->bstate, onEvent, userCtx, data,
length, NULL, 0, 0, 0, flags);
// 重置 scratch->core_info.exhaustionVector
clearEvec(rose, scratch->core_info.exhaustionVector);
if (!length) {
if (rose->boundary.reportZeroEodOffset) {
roseRunBoundaryProgram(rose, rose->boundary.reportZeroEodOffset, 0,
scratch);
}
goto set_retval;
}
if (rose->boundary.reportZeroOffset) {
int rv = roseRunBoundaryProgram(rose, rose->boundary.reportZeroOffset,
0, scratch);
if (rv == MO_HALT_MATCHING) {
goto set_retval;
}
}
if (rose->minWidthExcludingBoundaries > length) {
// 目标数据太少
goto done_scan;
}
if (rose->maxBiAnchoredWidth != ROSE_BOUND_INF
&& length > rose->maxBiAnchoredWidth) {
// 对全部双边锚定的模式串,数据超过了模式串设限的最大长度
goto done_scan;
}
// 若目标数据足够小,则使用 small write engine (Rose 引擎的一部分)
if (rose->smallWriteOffset) {
const struct SmallWriteEngine *smwr = getSmallWrite(rose);
if (length < smwr->largestBuffer) {
runSmallWriteEngine(smwr, scratch);
goto done_scan;
}
}
switch (rose->runtimeImpl) {
default:
assert(0);
case ROSE_RUNTIME_FULL_ROSE:
rawBlockExec(rose, scratch);
break;
case ROSE_RUNTIME_PURE_LITERAL:
pureLiteralBlockExec(rose, scratch);
break;
case ROSE_RUNTIME_SINGLE_OUTFIX:
soleOutfixBlockExec(rose, scratch);
break;
}
done_scan:
if (told_to_stop_matching(scratch)) {
unmarkScratchInUse(scratch);
return HS_SCAN_TERMINATED;
}
if (rose->hasSom) {
int halt = flushStoredSomMatches(scratch, ~0ULL);
if (halt) {
unmarkScratchInUse(scratch);
return HS_SCAN_TERMINATED;
}
}
if (rose->boundary.reportEodOffset) {
roseRunBoundaryProgram(rose, rose->boundary.reportEodOffset, length,
scratch);
}
set_retval:
hs_error_t rv = told_to_stop_matching(scratch) ? HS_SCAN_TERMINATED
: HS_SUCCESS;
unmarkScratchInUse(scratch);
return rv;
}
4.2 Rose 引擎匹配流程
void roseBlockExec(const struct RoseEngine *t, struct hs_scratch *scratch) {
/* 参数检查 */
......
const size_t length = scratch->core_info.len;
const char is_small_block = (length < ROSE_SMALL_BLOCK_LEN && t->sbmatcherOffset);
char *state = scratch->core_info.state;
init_for_block(t, scratch, state, is_small_block);
struct RoseContext *tctxt = &scratch->tctxt;
// 对于小块数据扫描,用一个联合 HWLM 匹配替代锚定、浮动匹配
if (is_small_block) {
const void *sbtable = getSBLiteralMatcher(t);
size_t sblen = MIN(length, t->smallBlockDistance);
// Match strings in table
hwlmExec(sbtable, scratch->core_info.buf, sblen, 0, roseCallback,
scratch, tctxt->groups);
} else {
runEagerPrefixesBlock(t, scratch);
if (roseBlockAnchored(t, scratch)) {
return;
}
if (roseBlockFloating(t, scratch)) {
return;
}
}
if (cleanUpDelayed(t, scratch, length, 0) == HWLM_TERMINATE_MATCHING) {
return;
}
// Catches up NFAs and the MPV
roseCatchUpTo(t, scratch, length);
if (!t->requiresEodCheck || !t->eodProgramOffset) {
DEBUG_PRINTF("no eod check required\n");
return;
}
if (can_stop_matching(scratch)) {
DEBUG_PRINTF("bailing, already halted\n");
return;
}
// 运行 EOD 扫描
roseBlockEodExec(t, length, scratch);
}
